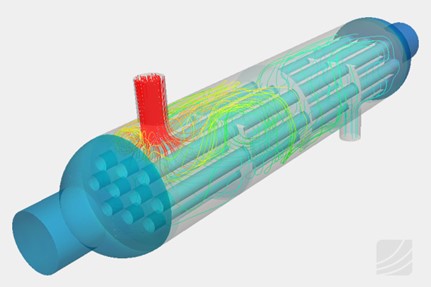
Temperature regulation units are vital components in many industrial processes, transferring heat between two fluids without allowing them to mix. Despite their robust design and efficiency, shell and tube heat exchangers can encounter several operational issues that affect their performance. Understanding how to troubleshoot these problems can help you maintain optimal efficiency and avoid costly downtime.
This guide will provide practical steps to diagnose and resolve common problems, such as pressure drops and thermal inefficiency, ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Identifying Pressure Drops
Pressure drops are one of the most common issues faced with these devices. A significant pressure drop can indicate a blockage, fouling, or improper flow rates, leading to reduced efficiency and potential system failure. Here’s how to address this issue:
Check for Fouling or Scaling: Over time, fouling and scaling can build up on the tube walls, restricting fluid flow and causing pressure drops. This is particularly common in environments with hard water or where the fluids contain suspended particles. To resolve this, consider scheduling regular cleaning or using anti-fouling treatments to minimize buildup.
Inspect for Blockages: Blockages can occur due to debris, corrosion, or improperly sized components. Inspect the tubes and shell for any obstructions, and ensure that filters and strainers are clean and functioning correctly. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help prevent blockages before they become severe.
Evaluate Flow Rates: Incorrect flow rates can also cause pressure drops. If the flow is too low, it may lead to an imbalance between the shell side and tube side, reducing the system’s efficiency. Make sure that the flow rates are within the recommended range specified by the manufacturer. Adjusting the pump speed or flow control valves can help optimize performance.
Addressing Thermal Inefficiency
Thermal inefficiency occurs when the device fails to transfer heat effectively between the fluids. This can be due to several factors, including fouling as suggested above, incorrect flow rates, or issues with the heat transfer surface.
Fouling and Scaling Impact: As mentioned earlier, fouling and scaling can severely affect the thermal performance of the system. When the tube surfaces are coated with deposits, the heat transfer rate decreases, leading to thermal inefficiency. Regular cleaning and using appropriate water treatment solutions can help maintain clean surfaces and efficient heat transfer.
Imbalance in Fluid Flow: If the flow rates of the two fluids are not balanced, it can lead to improper temperature exchange. For instance, if the flow rate on one side is too high or too low, it can reduce the heat transfer efficiency. Ensure that both fluids are flowing at optimal rates and that the inlet and outlet temperatures are within the desired range.
Inspecting the Heat Transfer Surface: The condition of the heat transfer surface plays a critical role in thermal efficiency. Any damage or wear to the surface can reduce heat transfer. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for corrosion, pitting, or any other surface damage. If necessary, replace damaged tubes or plates to restore efficiency.
Dealing with Tube Leaks
Tube leaks are another common issue that can compromise the performance and safety of the product. Leaks can allow fluids to mix, leading to contamination, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards.
Detecting Leaks Early: Regular pressure testing and visual inspections can help detect leaks before they become severe. Look for signs of moisture, corrosion, or unusual pressure fluctuations that may indicate a leak. Implementing a leak detection system can also provide early warnings.
Repairing or Replacing Tubes: If a leak is detected, it’s essential to repair or replace the affected tubes promptly. In some cases, a temporary fix, such as plugging the leaking tube, may be sufficient. However, for long-term reliability, replacing the damaged tubes is usually the best option. Be sure to use materials that are compatible with the operating environment to prevent future leaks.
Preventing Future Leaks: To minimize the risk of future leaks, ensure that the materials used in your system are resistant to corrosion and wear. Regularly inspect for signs of wear and consider implementing corrosion-resistant coatings or selecting materials with higher durability.
Addressing Vibration Issues
Vibration is another issue that can affect the performance and longevity of a heat tube. Excessive vibration can lead to tube damage, leaks, and even structural failure.
Identify the Source of Vibration: Vibration can be caused by factors such as flow-induced turbulence, improper installation, or mechanical issues. Inspect the system for loose components, misaligned parts, or any other mechanical problems that could cause vibration.
Implementing Dampening Solutions: To reduce vibration, consider installing dampening systems or supports that can absorb and minimize the impact. Ensuring proper installation and alignment of components can also help reduce vibration.
Monitor for Ongoing Issues: Regularly monitor the system for signs of vibration and address any issues promptly. Over time, even minor vibrations can lead to significant damage if left unchecked.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance is key to preventing and addressing issues. Implementing a preventive maintenance program can help you identify problems before they lead to system failures.
Scheduled Cleaning and Inspections: Regular cleaning, particularly of the tube surfaces, can prevent fouling and scaling. Scheduled inspections for leaks, corrosion, and other issues can also help maintain optimal performance.
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor the performance of the system, including pressure drops, temperature differences, and flow rates. Any deviations from the normal operating parameters should be investigated and addressed promptly.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting issues require a systematic approach, from identifying the root cause of the problem to implementing appropriate solutions. Whether dealing with pressure drops, thermal inefficiency, tube leaks, or vibration, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure reliable and efficient operation. By following these practical guidelines, you can keep your system running smoothly and avoid costly downtime.