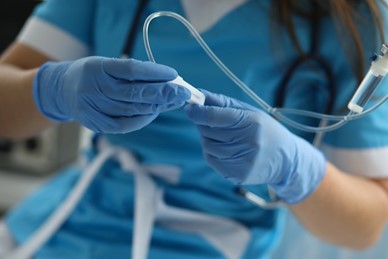
The medical device industry is undergoing a transformative period marked by groundbreaking innovations and advanced materials. As healthcare continues to evolve, the need for devices that enhance patient outcomes while ensuring safety and reliability is more critical than ever. Among the various materials used in medical device design, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE tubing) has emerged as a standout choice, particularly in applications such as catheters and drug delivery systems. This article explores the role of advanced materials like these in driving innovation in medical devices, focusing on their benefits and implications for the industry.
The Importance of Advanced Materials in Healthcare
Medical devices are subject to rigorous standards and regulations, ensuring they are safe, effective, and reliable. The choice of materials plays a crucial role in achieving these objectives. Advanced materials not only meet the stringent requirements of biocompatibility but also contribute to the functionality and performance of medical devices. As the demand for minimally invasive procedures and personalized medicine rises, materials that offer flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals are essential.
A Material of Choice
Polytetrafluoroethylene is a high-performance plastic known for its unique properties, making it an ideal candidate for various medical applications. Its biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and flexibility enable its use in devices that come into direct contact with bodily fluids. This material is particularly valuable in applications such as:
Catheters: Catheters are used for a range of procedures, from urinary to cardiovascular applications. The flexibility of the tubing allows for smooth navigation through the body’s intricate pathways, reducing the risk of injury and discomfort. Additionally, its resistance to friction minimizes the chance of complications, making it a preferred material for catheter design.
Drug Delivery Systems: The growing trend toward targeted and sustained drug delivery has led to innovations in delivery systems that utilize Polytetrafluoroethylene. Its non-reactive nature ensures that drugs remain stable during transport, while its ability to be fabricated into various forms allows for customizable delivery mechanisms. For instance, this material can be used to create microcatheters that deliver medication directly to a specific site within the body, enhancing treatment efficacy.
The Benefits
One of the most critical factors in medical device design is biocompatibility. Devices made with PTFE are inert, meaning they do not react with bodily fluids, significantly reducing the risk of adverse reactions. This property is essential for devices that will remain in the body for extended periods.
These materials are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids and solvents. This resistance ensures that the integrity of medical devices is maintained, preventing degradation over time. In applications like drug delivery systems, this characteristic is vital to ensure that the drug remains stable and effective until it reaches its target.
The flexibility allows for the design of devices that can navigate through the body’s complex anatomy without causing damage. Moreover, its durability means that devices can withstand the stresses associated with insertion and movement within the body.

Innovations
The advancements in medical devices facilitated by high-performance materials have paved the way for numerous innovations:
Minimally Invasive Techniques: The rise of minimally invasive surgical techniques has led to the development of new devices that incorporate these advanced materials. These techniques reduce recovery times and patient discomfort while enhancing surgical precision.
Customized Solutions: Advances in manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, allow for the production of customized medical devices tailored to individual patient needs. The versatility makes it suitable for these applications, enabling the creation of devices that match specific anatomical requirements.
Smart Medical Devices: The integration of technology into medical devices has resulted in the emergence of smart devices that monitor patient health in real-time. It can be used in these devices due to its biocompatibility and ability to work alongside sensors and electronics.
The Future of Medical Devices
As the medical device industry continues to innovate, the role of advanced materials ill only grow. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring new polymers and composites that offer improved performance and safety. The focus on patient-centered care will drive the demand for devices that are not only effective but also enhance the overall patient experience.
Conclusion
The innovations in medical device design are profoundly influenced by advanced materials. Their unique properties make it an invaluable resource in applications like catheters and drug delivery systems, where biocompatibility, flexibility, and chemical resistance are paramount. As the industry moves toward more sophisticated, personalized, and minimally invasive solutions, the importance of materials that can meet these challenges will be central to the future of medical technology. By harnessing the potential of advanced materials, the medical device sector is poised to improve patient outcomes and revolutionize healthcare delivery.